Chapter 8 – Slice Or Dice: What Are The Surgical Treatment Options For Hip Pain?
Chapter 8 – Slice Or Dice: What Are The Surgical Treatment Options For Hip Pain?

- Slice Or Dice
- Just What Is Involved With Total Hip Replacement Surgery?
- Watch An Animated Video Of A Total Hip Replacement
- High School Shop Class
- How Long Will The ‘Minor’ Hip Replacement Surgery Take?
- What Is The Percentage Of Success For Hip Replacement Surgery?
- What Is The Percentage Of Failure For Hip Replacement Surgery?
- Cement Or Cementless?
- Smooth Operator: Who Will Perform Your Surgery?
- These Guys And Gals Are Smart
- And A Cast Of Thousands
- Knock Yourself Out: What Type Of Anesthesia Should You Have During Surgery?
- Put To Sleep
- Just How Many Ways Are There To Perform Hip Replacement Surgery?
- Hip Replacement Surgery: Glue Or Stitches Or Staples?
- Standard-Length Incision Surgery
- Small Incision Surgery
- No Pain, No Gain

Slice Or Dice – This is the ‘slice’ in slice or dice, meaning you have elected to have your hip surgically treated.
Total Hip Replacement Process
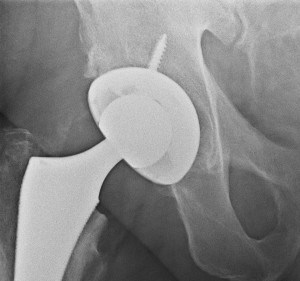
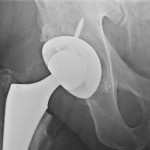
Just What Is Involved With Total Hip Replacement Surgery? A total hip replacement operation is a surgical procedure in which an incision is made to expose your femur and hip to remove the arthritic ball of your upper thigh bone (femur), and damaged cartilage from the hip socket. Just so you know, the head of your femur is surgically sawed off and your surgeon will then drill a hole in your femur so they can insert the prosthesis solidly inside your femur.
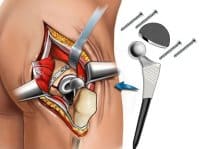
After the prosthesis is inserted into your femur, a receiving socket is screwed into your hip. The prosthesis and socket are designed to resist corrosion, degradation, wear, and pain.
Watch An Animated Video Of A Total Hip Replacement – There are many graphic videos of cutting, dislocating, suturing, etc. on YouTube. I have included a well-made, animated, three-minute video for you to watch on hip replacement surgery.
High School Shop Class – So far, this sounds like what I learned in my high school shop class: cut, saw, glue, and screw. Sometimes, the prosthetic metal ball and stem may be glued to the inside of your femur bone with acrylic cement. Many times, no glue is used. The socket is usually replaced with a plastic liner that is fixed inside a metal shell. The metal shell of the socket is usually fixed tightly to your bone without glue.
Socket receptacle
Hip Replacement Prosthetic
In my case, a screw was used to hold the socket shell in place. The artificial ball and socket relieves the bones from rubbing and, therefore, the pain is usually relieved.
“I learned a long time ago that minor surgery is when they do the operation on someone else, not you.”
Bill Walton (discussing his 36+ surgeries)
How Long Will The ‘Minor’ Hip Replacement Surgery Take? A typical hip replacement surgery takes averages about 90 minutes. It can be as short as 60 minutes or the surgery can exceed three hours. You need to add surgery prep and surgery recovery time to your total experience. My surgery ran almost two-and-a-half hours, plus recovery. Regardless, the process is so quick that some even call it a minor surgery nowadays.
9.4
- Brand: Drive Medical
- Color: Silver
- Material: Aluminum
- Item Weight: 7.5 lbs.
- Weight Limit: 350 lbs.
- Item Dimensions: LxWxH 17.5 x 24 x 32 inches
9.4
Rod’s Comments: I still use these to this very day.
- Interchangeable Tips: Swap out the tips quickly and easily
- Colors: Multiple colors available
- Adjustable Length: From 24.5 – 54 inches
- Comfortable: Anti-slip cork handles
8.6
- Brand: Safe-er-Grip
- Material: Plastic
- Color: White/Grey
- Item Weight: 0.9 lbs.
- Weight Limit: 200 lbs.
- Item Dimensions: LxWxH 16.5 x 4 x 3.75 inches
What Is The Percentage Of Success For Hip Replacement Surgery? While no one likes to have a surgical procedure, hip replacement surgery has a very high rate of success. It is estimated that about 90% of all patients experience either great or total pain relief. In my case, I experienced a near-complete eradication of pain. The discomfort I had during the first ten weeks was really from post-surgical pain and not from the hip itself.

What Is The Percentage Of Failure For Hip Replacement Surgery? Not everything always works out as planned, as 10% of patients find either minor relief and some find even worse pain. Unfortunately, we have a friend who was a former college basketball and volleyball player and required a hip replacement at 35 years of age. She says she has received minimal relief and that some mornings it still takes her five minutes to get out of bed.
Cement Or Cementless? Your orthopedic surgeon will determine if your hip replacement will use the cemented version to secure the prosthetic or if you will rely on bone growth for securing your transplant.
Initially, I thought for sure that cement would be the right call for me, but it wasn’t. Cement may be good for house foundations and keeping Jimmy Hoffa from being found, but the weak link for most hip replacement patients is the cement bond between your implant and your bone. Your orthopod can add a porous, rough surface to the implant and eliminate the need for bone cement, which then provides a natural bond between the implant and bone. You will be informed of this option, but mostly it won’t be your decision.
Smooth Operator: Who Will Perform Your Surgery? An orthopedic surgeon will be responsible for your hip replacement surgery. In America, orthopedic surgeons have typically completed four years of undergraduate education and then completed four years of medical school. After those eight years, a physician desiring to become an orthopedic surgeon typically undertakes residency training in orthopedic surgery lasting five years.
These Guys And Gals Are Smart – In the United States, there are approximately 700 physicians completing an orthopedic residency training each year. Just ten percent of current orthopedic surgery residents are women. It is estimated there are over 20,000 actively practicing orthopedic surgeons. In case the four years of college, four years of medical school, and five years of residency isn’t enough, many orthopedic surgeons complete additional training, or fellowships, after completing their residency training. A fellowship allows a physician to receive orthopedic sub-specialty training, including hip replacements.
And A Cast Of Thousands – Your orthopedic surgeon will be typically be assisted by physician assistants, residents, fellows and possibly other physicians. Additionally there will be operating room nurses and a multitude of other health care professionals available in case you require their talents. And, of course, billing and insurance personnel.
Knock Yourself Out: What Type Of Anesthesia Should You Have During Surgery? Patients often wonder if they need to be put to sleep for this surgery: Umm, yep! You will first have regional anesthesia. There are multiple types of regional anesthesia available including spinal block, epidural block, and peripheral nerve block. You will meet with your anesthesiologist to determine which is best for you.
Put To Sleep – After your hip area is numbed to pain, you can opt to either stay alert during the operation (not suggested unless you want to update your Facebook page in real time) or you will receive IV sedation, which means you are totally unaware of anything during your surgery. Some patients may opt for general anesthesia which is what most consider ‘being put to sleep.’ Fortunately, this version of ‘put to sleep’ has a better outcome than when we take our beloved pets to a vet.
“How do I love thee? Let me count the ways.”
Elizabeth Barrett Browning
Just How Many Ways Are There To Perform Hip Replacement Surgery? There are many approaches to how an orthopedic surgeon will lovingly repair your hip. There are several incisions, defined by their relation to the gluteus medius. The approaches are posterior, lateral, antero-lateral, anterior, and greater trochanter osteotomy. Posterior is currently the most commonly used approach. The incision is made from the back of the hip. Small, non-critical tendons are skillfully detached to allow your orthopod access to your hip joint and then are later re-attached during the operation.
Anterior surgery, the front of the hip incision, is becoming more common.
The type of surgery you receive will be based on your medical condition and the preferred method of your physician.
“Pain heals, chicks dig scars, glory lasts forever.”
The Replacements – Keanu Reeves
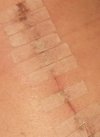
Hip Replacement Surgery: Glue Or Stitches Or Staples? – Hip replacement surgery incisions can be glued, stitched or stapled. Which is best for you?
Stapled Sutures
Glued Sutures
My surgery scar was closed using surgical glue, no staples.
Hip Replacement Surgery Incisions – Hip replacement surgery involves one of two types of incisions: standard-length incisions and small incisions.
- Standard-Length Incision Surgery – This is by far the most common type of incision. The advantage for your physician, and indirectly you, is it allows greater access to your hip. The negative for this option is it involves a longer incision, meaning a longer scar.
- Small Incision Surgery – As you might imagine, small incision surgery is a smaller opening, and thus, a smaller scar. Initial studies have found no difference in recovery time between these two methods. Most of the difference revolves around whether you are male or female. Not surprisingly, most women prefer the small incision method.
While it is good to be aware of your surgical treatment options, the final decision will be with your orthopedic surgeon. They will understand which procedure is best for your medical condition.
No Pain, No Gain – There will be some pain associated with your surgery. You will notice pain as your surgical nerve block wears off. The hospital staff will work to manage your pain and you will receive pain medicine as needed. Your personal gain is your hip pain subsiding and that the post-surgery pain will soon dissolve as well.
Alrighty… that concludes Chapter 8.